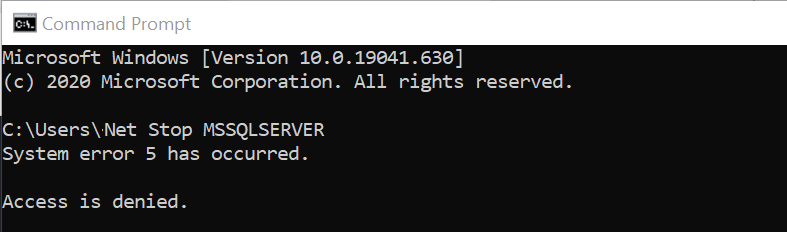
Hello there! This article is about Junior SQL DBA Interview Q&A. Please go through the first article of this Interview question answers series Junior SQL DBA Interview Q&A
By the way though it is about Junior SQL DBA Interview, you may get these questions for mid to senior level DBAs as well.
Junior SQL DBA Interview Q&A:
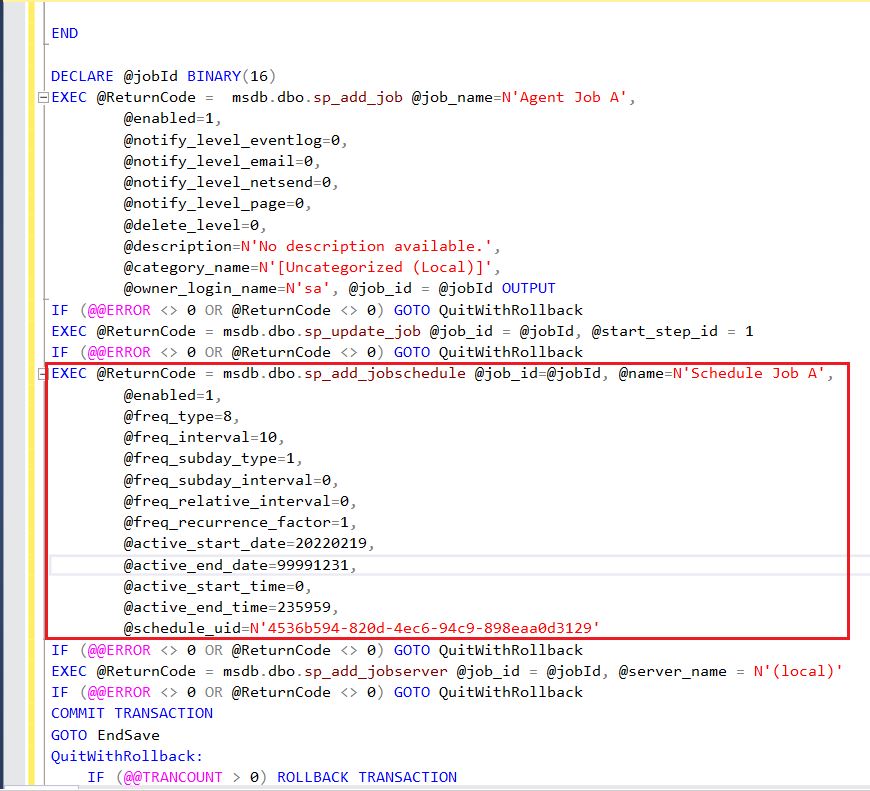
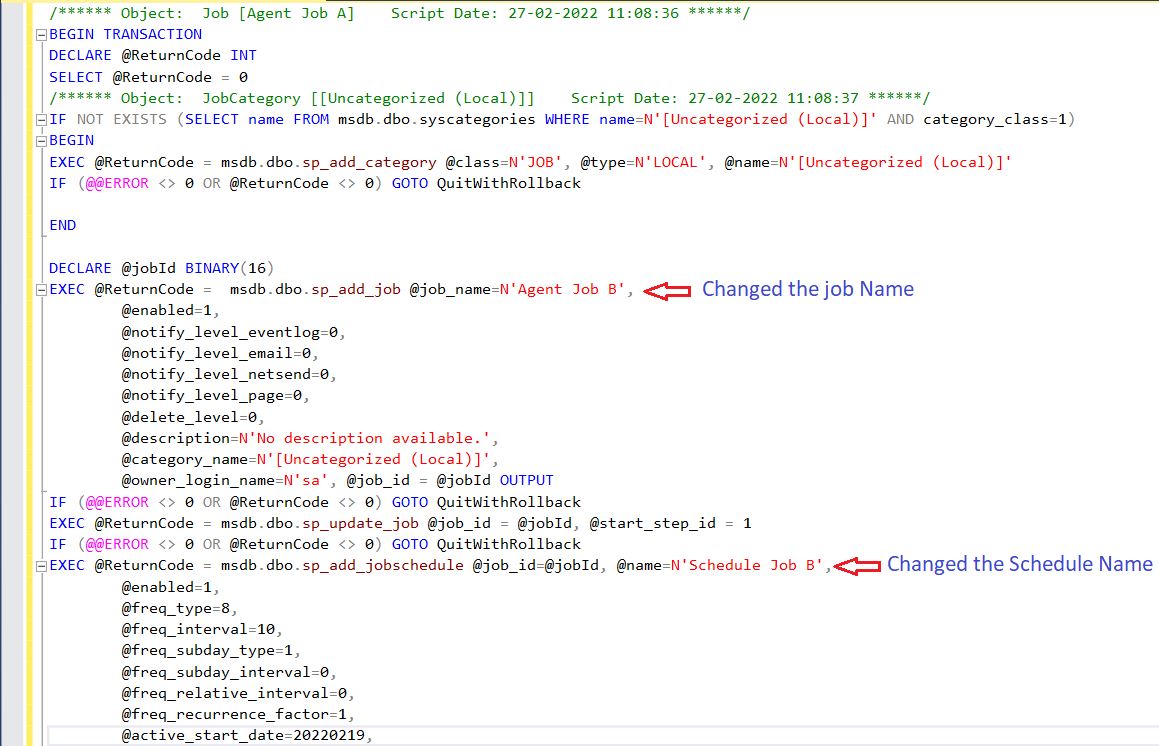
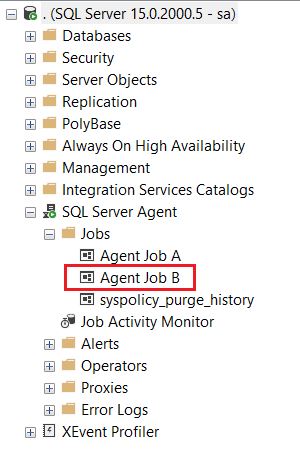
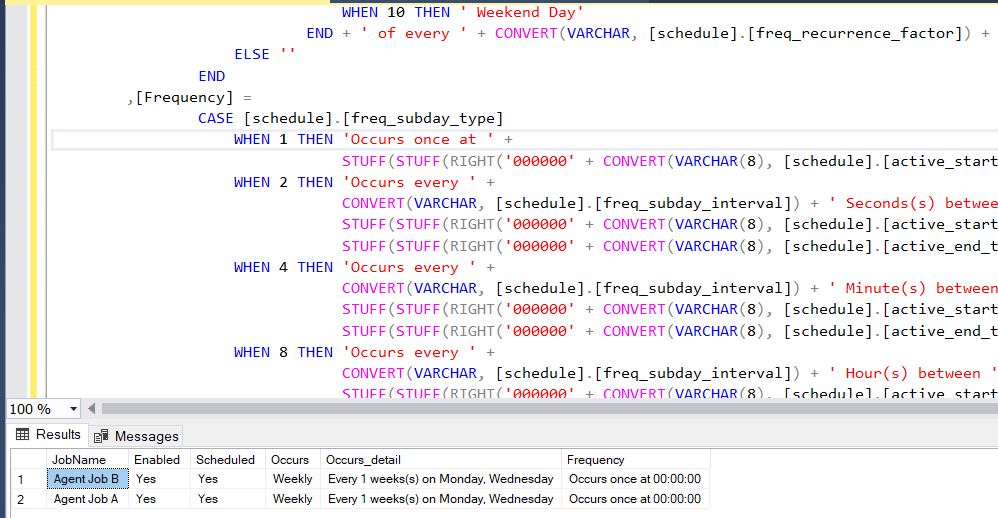
1.What are the recovery models in SQL Server?
Ans: Simple, Full and Bulk Logged Recovery Model.
2. Explain the Recovery Models and the difference between them?
Ans: The database recovery model setting affects the retention of transaction log entries. The database logs every transaction into the transaction log file irrespective of the recovery model.
But the recovery model determines when SQL Server can truncate (remove/delete)these transactions from the log file. Whether you can take transaction log backup and the kinds of restore operations.
Simple:
SQL Server automatically truncates all the committed transactions from the log file when checkpoint occurs.
Each transaction is still written to the transaction log. (Most junior folks have this confusion). Simple recovery logs every transactions and not like because it is says “simple” it does not log all transactions.
It supports the following backup types:
- Full backup
- Differential backup
- Copy-Only backup
- File backup
- Partial backup
Now since checkpoint removes the log records, it does not supports transaction log backups. And hence point-in-time restores cannot be performed.
Full:
SQL Server truncates the log only after transaction log backup. Most importantly, just like the simple recovery model, it writes all transactions to the transaction log file.
But the main difference is the transactions stays in the log file until a transaction log backup is taken.
It supports all backup types:
- Full backup
- Differential backup
- Transaction log backup
- Copy-Only backup
- File and/or file-group backup
- Partial backup
Since Full recover model writes every transaction to the transaction log, it supports point-in-time restores.
Bulk Logged:
Bulk-logged recovery model functions similar to the full recovery model with the exception that it minimally logs the transactions log records.
Hence it also truncates the log only after transaction log backup. It also supports all backup types.
The bulk-logged recovery model minimizes transaction log space usage during bulk-logged operations like BULK INSERT, SELECT INTO, or CREATE INDEX .
Because it minimally logs the bulk-logged operations, it affects point-in-time recoveries. Read it Again. I didn’t mention that you can’t perform point-in-time recovery.
This is again a misconception. Always remember you can still do a point-in-time restore just like you can in the full recovery model only if no bulk-logged operations are performed at all when the database is using bulk logged recovery model.
3. How recovery model impacts database backups?
Ans: Since recovery model settings determines when the logged transactions are removed from log file it impacts the backup types.
As explained above because log records are removed when a checkpoint occurs, transaction log backups are not supported when using the simple recovery model.
On the other hand in Full recovery model log records are not auto removed when a checkpoint occurs, hence it supports transaction log backups along with Full and Differential.
Bulk logged recovery model behaves exactly like Full recovery model. Hence it supports all backup types.
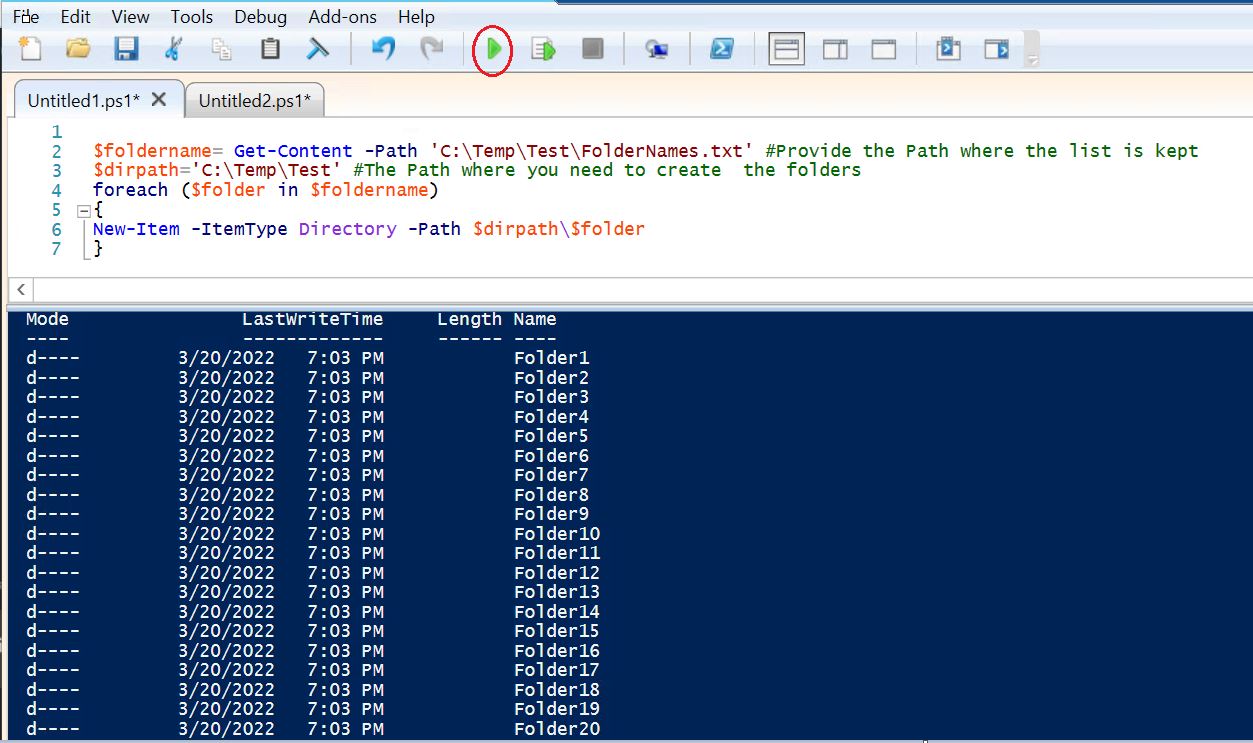
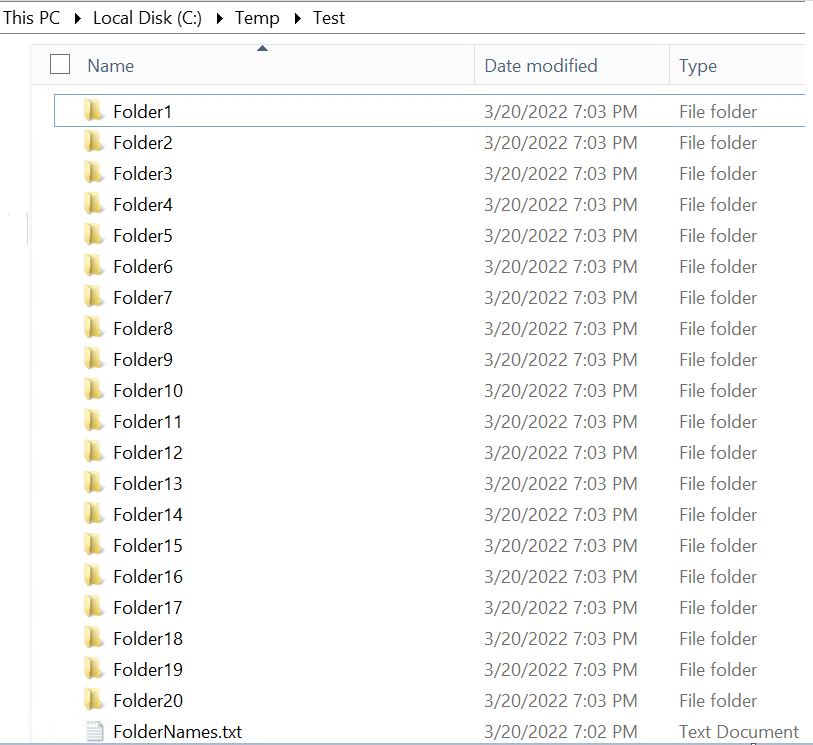
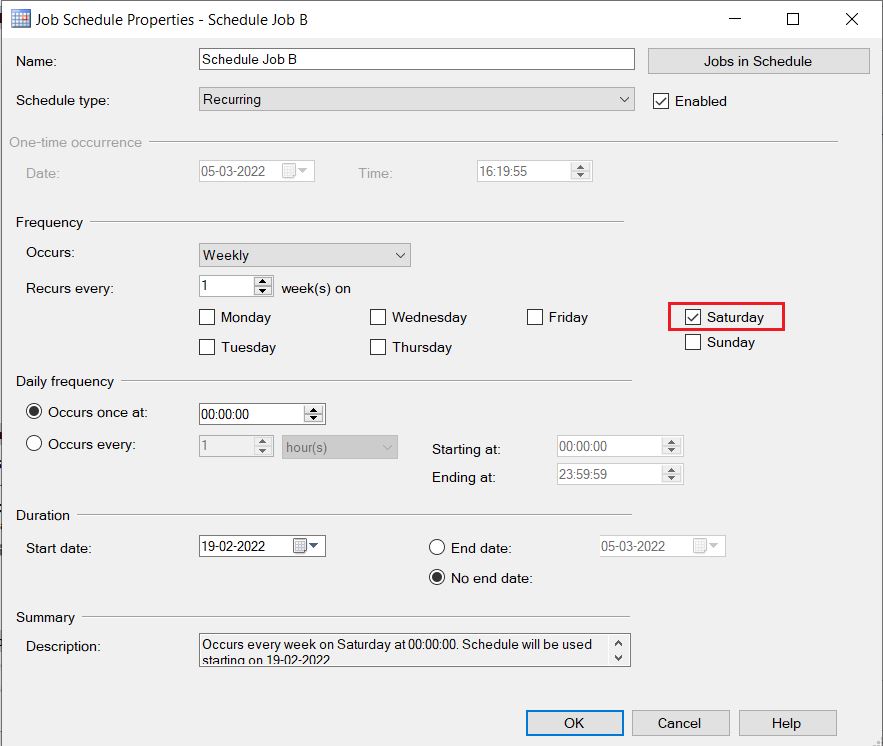
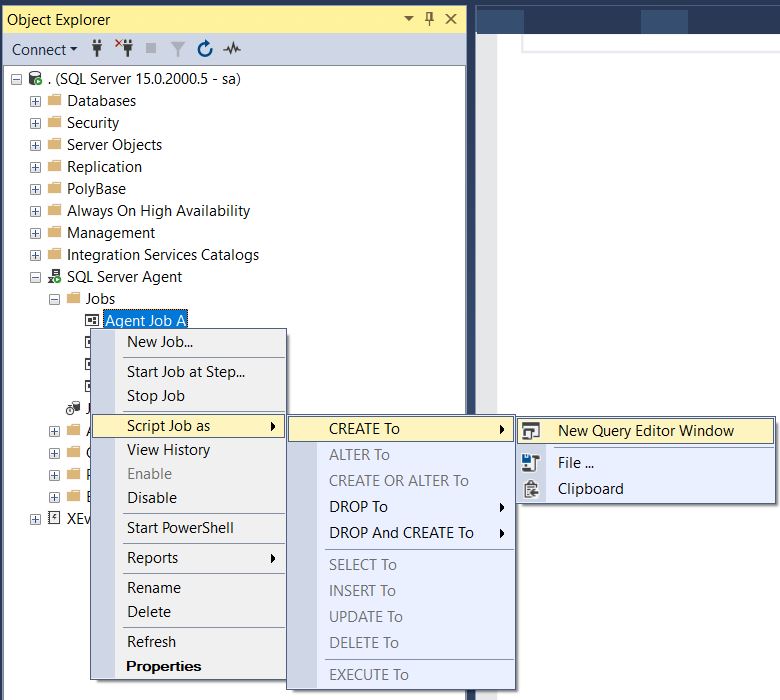
4. How to check the recovery model of a database?
Ans: There are multiple ways to determine the recovery model of a database. One is to use SQL Server Management Studio tool (SSMS). Another is using T-SQL Code.
Using SSMS:
First right-click on a database, then select the “Properties” item from the drop-down.
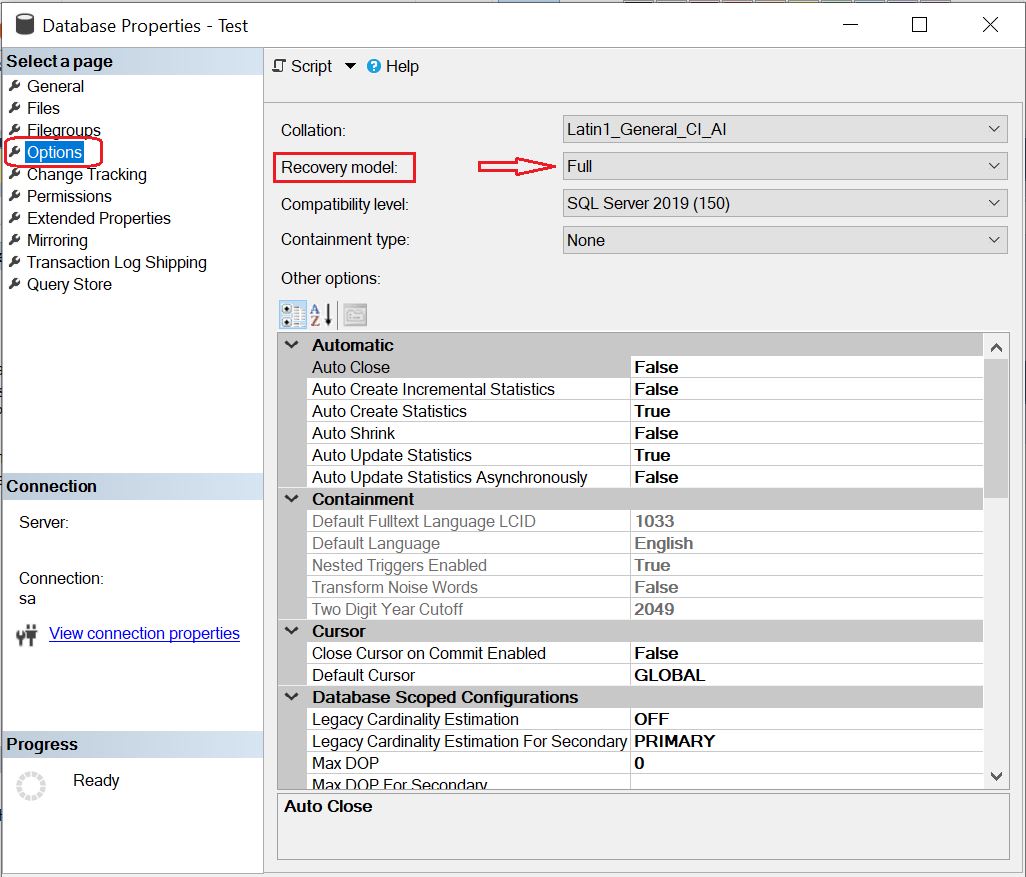
Now from database properties, select the “Options” item from the left context menu. The window will display as shown below:
Using T-SQL Code:
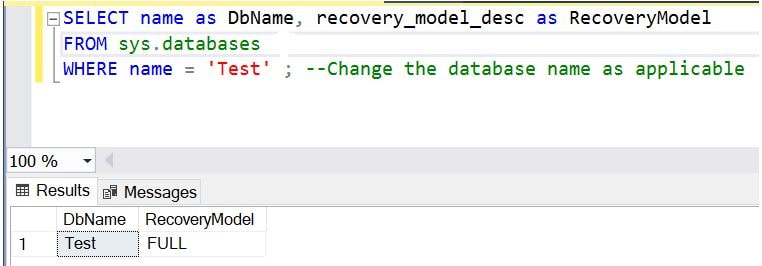
SELECT name as DbName, recovery_model_desc as RecoveryModel FROM sys.databases WHERE name = 'Test' ; --Change the database name as applicable
Result:
5. How to change the recovery model of a database?
Ans: In the same fashion as described above, there are two ways to change the recovery model. One is through SSMS and second is through T-SQL Code.
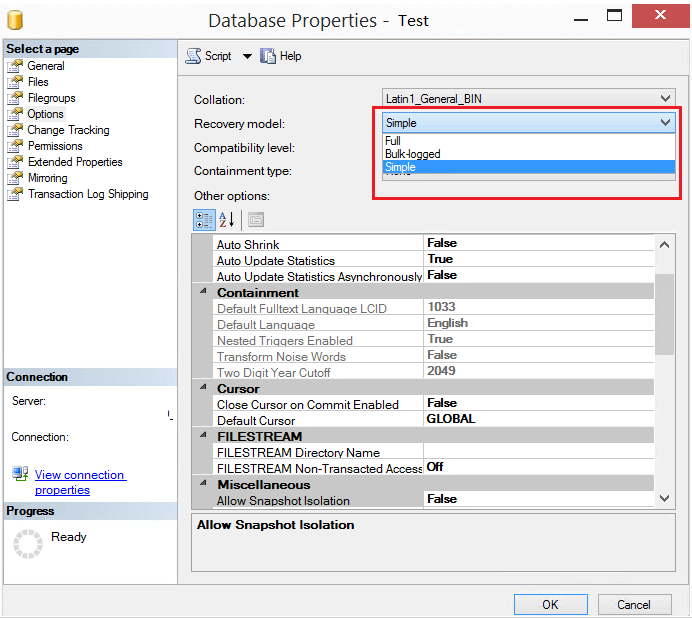
Using SSMS:
Go to database properties as shown in the answer for question no. 4 and use the dropdown menu to change the recovery model:
Using T-SQL Code:
USE [master] ; ALTER DATABASE [Test] SET RECOVERY SIMPLE
6. What are the Network Protocols Supported by SQL Server?
Ans:
- Shared Memory
- Named Pipes
- TCP/IP
- VIA
Shared Memory:
Clients can use Shared Memory protocol only to connect to a SQL Server Instance installed on the same server. You can use this protocol for troubleshooting when you suspect other protocols are not working as per expectation.
Failover Clusters does not support this protocol.
Named Pipes:
Basically used by Clients to connect to a SQL Server Instance in the same LAN (Local Area Network). It facilitates Inter-process communication for the machines in the same LAN. That is output of one process is input for the other. Also you can configure the SQL Server instance to listen to one pipe only.
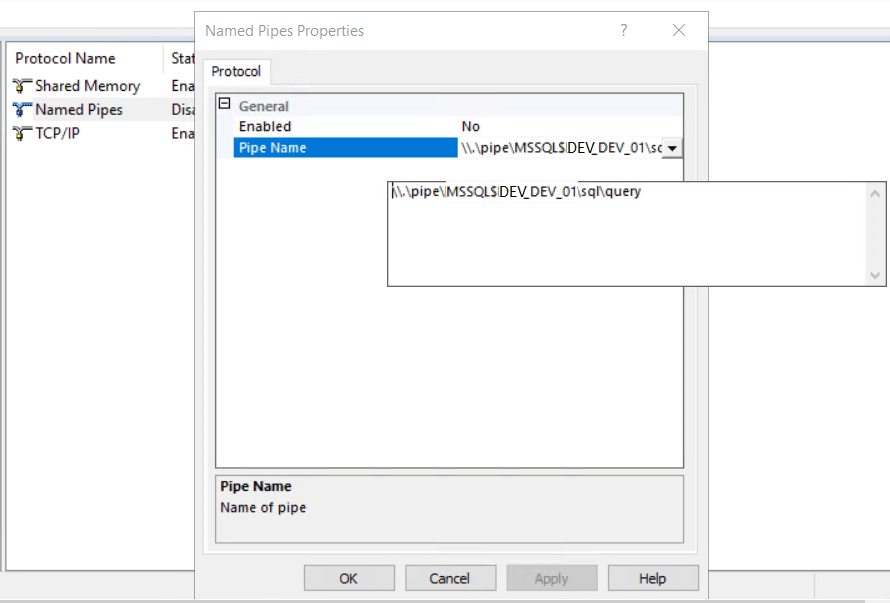
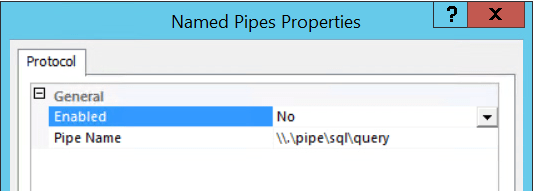
Below Example screen shots shows named pipe for Named and Default Instance :
Named Instance:
Default Instance:
TCP\IP:
This is the most popular and common protocol. It empowers client to connect to SQL Instance over the Internet (WAN/Any Server within interconnected Network). This protocol includes network traffic routing standards with advanced security protection, connects computers with different hardware and operating systems configurations.
VIA:
Virtual Interface Adapter protocol is used to support VIA devices such as VIA Storage Area Network devices. This protocol supported high performance, clustering, and load-balancing on dedicated network connections. Microsoft already deprecated this feature.