This article is to keep a handy script to list SQL Agent Jobs and Schedules. In the previous article I had provided a script to change the job schedule. This script may be very next one you need.
Once we changed the job schedules in all SQL Servers in the environment, we needed a script to verify. There are many scripts available in the net. Hence I kind of tweaked one of the script. It’s been long time and hence not able to provide the original source.
Note:Please change the Job Names in the Where clause of the query to verify the job schedule of the jobs you made changes to.
Query to get list of jobs in sql server with schedules
SELECT [JobName] = [jobs].[name]
,[Enabled] = CASE [jobs].[enabled] WHEN 1 THEN 'Yes' ELSE 'No' END
,[Scheduled] = CASE [schedule].[enabled] WHEN 1 THEN 'Yes' ELSE 'No' END
,[Occurs] =
CASE [schedule].[freq_type]
WHEN 1 THEN 'Once'
WHEN 4 THEN 'Daily'
WHEN 8 THEN 'Weekly'
WHEN 16 THEN 'Monthly'
WHEN 32 THEN 'Monthly relative'
WHEN 64 THEN 'When SQL Server Agent starts'
WHEN 128 THEN 'Start whenever the CPU(s) become idle'
ELSE ''
END
,[Occurs_detail] =
CASE [schedule].[freq_type]
WHEN 1 THEN 'O'
WHEN 4 THEN 'Every ' + CONVERT(VARCHAR, [schedule].[freq_interval]) + ' day(s)'
WHEN 8 THEN 'Every ' + CONVERT(VARCHAR, [schedule].[freq_recurrence_factor]) + ' weeks(s) on ' +
LEFT(
CASE WHEN [schedule].[freq_interval] & 1 = 1 THEN 'Sunday, ' ELSE '' END +
CASE WHEN [schedule].[freq_interval] & 2 = 2 THEN 'Monday, ' ELSE '' END +
CASE WHEN [schedule].[freq_interval] & 4 = 4 THEN 'Tuesday, ' ELSE '' END +
CASE WHEN [schedule].[freq_interval] & 8 = 8 THEN 'Wednesday, ' ELSE '' END +
CASE WHEN [schedule].[freq_interval] & 16 = 16 THEN 'Thursday, ' ELSE '' END +
CASE WHEN [schedule].[freq_interval] & 32 = 32 THEN 'Friday, ' ELSE '' END +
CASE WHEN [schedule].[freq_interval] & 64 = 64 THEN 'Saturday, ' ELSE '' END ,
LEN(
CASE WHEN [schedule].[freq_interval] & 1 = 1 THEN 'Sunday, ' ELSE '' END +
CASE WHEN [schedule].[freq_interval] & 2 = 2 THEN 'Monday, ' ELSE '' END +
CASE WHEN [schedule].[freq_interval] & 4 = 4 THEN 'Tuesday, ' ELSE '' END +
CASE WHEN [schedule].[freq_interval] & 8 = 8 THEN 'Wednesday, ' ELSE '' END +
CASE WHEN [schedule].[freq_interval] & 16 = 16 THEN 'Thursday, ' ELSE '' END +
CASE WHEN [schedule].[freq_interval] & 32 = 32 THEN 'Friday, ' ELSE '' END +
CASE WHEN [schedule].[freq_interval] & 64 = 64 THEN 'Saturday, ' ELSE '' END
) - 1
)
WHEN 16 THEN 'Day ' + CONVERT(VARCHAR, [schedule].[freq_interval]) + ' of every ' + CONVERT(VARCHAR, [schedule].[freq_recurrence_factor]) + ' month(s)'
WHEN 32 THEN 'The ' +
CASE [schedule].[freq_relative_interval]
WHEN 1 THEN 'First'
WHEN 2 THEN 'Second'
WHEN 4 THEN 'Third'
WHEN 8 THEN 'Fourth'
WHEN 16 THEN 'Last'
END +
CASE [schedule].[freq_interval]
WHEN 1 THEN ' Sunday'
WHEN 2 THEN ' Monday'
WHEN 3 THEN ' Tuesday'
WHEN 4 THEN ' Wednesday'
WHEN 5 THEN ' Thursday'
WHEN 6 THEN ' Friday'
WHEN 7 THEN ' Saturday'
WHEN 8 THEN ' Day'
WHEN 9 THEN ' Weekday'
WHEN 10 THEN ' Weekend Day'
END + ' of every ' + CONVERT(VARCHAR, [schedule].[freq_recurrence_factor]) + ' month(s)'
ELSE ''
END
,[Frequency] =
CASE [schedule].[freq_subday_type]
WHEN 1 THEN 'Occurs once at ' +
STUFF(STUFF(RIGHT('000000' + CONVERT(VARCHAR(8), [schedule].[active_start_time]), 6), 5, 0, ':'), 3, 0, ':')
WHEN 2 THEN 'Occurs every ' +
CONVERT(VARCHAR, [schedule].[freq_subday_interval]) + ' Seconds(s) between ' +
STUFF(STUFF(RIGHT('000000' + CONVERT(VARCHAR(8), [schedule].[active_start_time]), 6), 5, 0, ':'), 3, 0, ':') + ' and ' +
STUFF(STUFF(RIGHT('000000' + CONVERT(VARCHAR(8), [schedule].[active_end_time]), 6), 5, 0, ':'), 3, 0, ':')
WHEN 4 THEN 'Occurs every ' +
CONVERT(VARCHAR, [schedule].[freq_subday_interval]) + ' Minute(s) between ' +
STUFF(STUFF(RIGHT('000000' + CONVERT(VARCHAR(8), [schedule].[active_start_time]), 6), 5, 0, ':'), 3, 0, ':') + ' and ' +
STUFF(STUFF(RIGHT('000000' + CONVERT(VARCHAR(8), [schedule].[active_end_time]), 6), 5, 0, ':'), 3, 0, ':')
WHEN 8 THEN 'Occurs every ' +
CONVERT(VARCHAR, [schedule].[freq_subday_interval]) + ' Hour(s) between ' +
STUFF(STUFF(RIGHT('000000' + CONVERT(VARCHAR(8), [schedule].[active_start_time]), 6), 5, 0, ':'), 3, 0, ':') + ' and ' +
STUFF(STUFF(RIGHT('000000' + CONVERT(VARCHAR(8), [schedule].[active_end_time]), 6), 5, 0, ':'), 3, 0, ':')
ELSE ''
END
FROM [msdb].[dbo].[sysjobs] AS [jobs] WITh(NOLOCK)
LEFT OUTER JOIN [msdb].[dbo].[sysjobschedules] AS [jobschedule] WITh(NOLOCK)
ON [jobs].[job_id] = [jobschedule].[job_id]
LEFT OUTER JOIN [msdb].[dbo].[sysschedules] AS [schedule] WITh(NOLOCK)
ON [jobschedule].[schedule_id] = [schedule].[schedule_id]
where [jobs].[name] in ('1_DBA job Name', '11_DBA job Name') -- Change the job names or add/remove as applicable
GO
Again please change the values for Where clause. I know it is a long query hence mentioning it again.
The OutPut of the above query

The query provides details on how the jobs are scheduled. If you want to to list the schedules of all the SQL Agent Jobs then just remove the where clause.
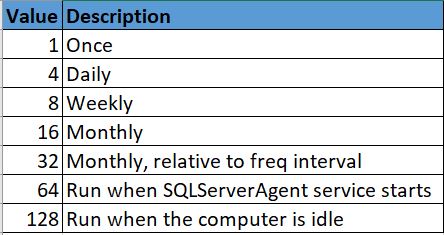
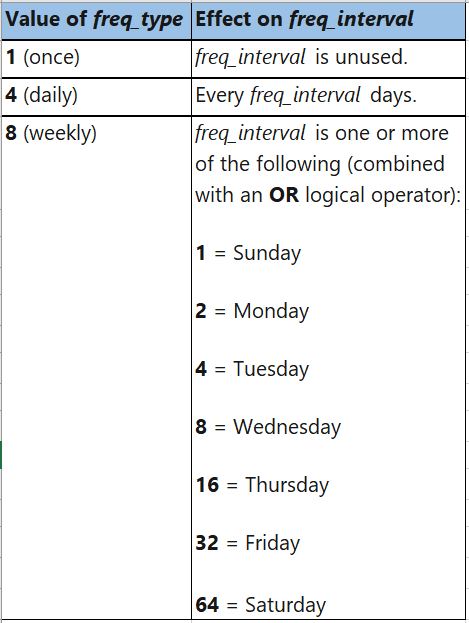
 freq_interval: The days that a job will execute.
freq_interval: The days that a job will execute.